Ever since COVID-19 hit the world, we learned several new things about our bodies, such as how our immune system fights against external viruses and by what means our bodies make antibody proteins to detect and protect us from foreign bacteria and viruses.
Besides, we also came to know about the test that identifies the active infections and in what way our body is coping with them.
Rapid antigen exams, also known as point-of-care tests (POCTs), are a type of immunoassay that can identify immunizers in human blood, serum, or other bodily fluids. They are quick and easy to use.
Also, they can be performed on-site and provide results within minutes. These examinations have the potential to revolutionize the way we diagnose illnesses and treat patients in developing countries.
Understanding What Rapid Antigen Tests Are

They are the future of antibody detection. These trials are not only faster than the previous generation of immunizer detection, but they also provide more accurate results.
Generally, rapid antigen tests are a relatively new technology in the medical field, having been around for only about a decade. Since their introduction, hospitals and clinics have begun to rely on them as an alternative to traditional blood examination diagnostics.
Antibodies are the molecules that help your immune system identify and attack foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses. They detect immunizers for certain diseases in a blood sample.
In addition, these assessments for HIV, hepatitis C, and other infectious diseases are available today.
If you have been exposed to a disease or are unsure if you have been exposed, they can tell you quickly if you need treatment and can be used for blood donations and organ transplants as well.
How and Why are Antigen Tests Performed?
The detection is used to determine people infected with infectious diseases from different types of viruses, including:
- COVID-19
- Infections caused by Streptococcus
- influenza A virus
- Malaria
- HIV
- Hepatitis C
These are usually administered by collecting samples from the patient’s nose or oral cavity and then mixing the sample with a chemical solution to obtain the results.
Here’s a quick rundown of the steps:
- Swab and rotate the swab inside both nostrils to collect the sample.
- Insert the swab into the well.
- Pour in the liquid chemical solution.
- Wait up to 15 minutes to see the results.
How Do Rapid Antigen Tests Work?
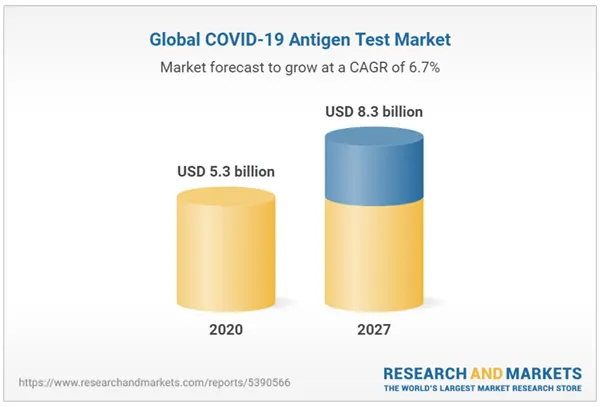
(This graph shows that the global COVID-19 antigen test market size is expected to reach $8.3 by 2027).
These trials are a type of immunoassay used to diagnose many diseases and conditions that use an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to encounter the presence of an antibody. They work by identifying the presence of an antigen in a sample.
The exam is performed similarly to traditional ELISA but is faster and simpler. This means that it can be used for screening purposes or to monitor changes in microbe levels over time.
The ELISA technique is often used in these tests because it is sensitive and can detect low concentrations of immunizers, even when they are present at very low levels.
They work by recognizing the presence of antibodies to a specific antigen in the blood. These immunizers are produced by the immune system when it is first exposed to a virus, and they help fight off an infection.
They spot these antibodies before an infection can take hold and cause symptoms or damage. These tests have been around since 1988, but they are still not widely used because they require a trained technician to process them.
This means that there is a need for more research on how these assessments work and their ability to be performed by untrained people.
Do You Know? Rapid antigen tests are less accurate than regular tests. They can only tell if we had a virus in the past, not in the present.
Conclusion
With the recent COVID-19 global pandemic, these tests have ignited growing interest in their use as a valuable screening aid, though several issues must be addressed.
However, their role as the future of antibody detection is undeniable, and scientists are working hard to see how it could influence the future of medicine.