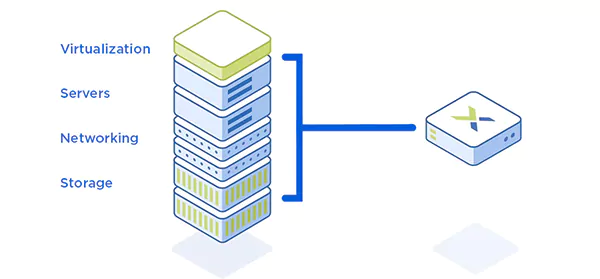
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI) combined with Software-Defined Architecture (SDA) is revolutionizing enterprise IT management. This combination enables organizations to consolidate computing, storage, and networking into a incorporated, software-driven system.
But don’t just take my word for it. As of 2021, the HCI market is valued at USD 11.2 billion and is projected to soar to USD 45.33 billion by 2027.
What you need to understand is that their group action is not merely a technological convergence but a strategic arrangement. This allows for enhanced resource administration, automated orchestration, and unified administration.
Scroll down to discover how appliances in Software-Defined Architecture can benefit your organization. But first, you’ll also learn about its fundamentals, business implications, and other key details.
The Fundamentals of Hyper-Converged Infrastructure
What is HCI?
Hyper-converged appliances simplify the existing IT infrastructure by combining computing, retention, and networking components into a single software-driven system. This reduces the direction complexity and long-term costs when increasing efficiency.
Statistics
The market size of Hyper Converged Infrastructure market was USD 5.88 billion in 2020. Later, it was projected to grow from USD 6.79 billion in 2021 to USD 32.19 billion by 2028. The growth was estimated at a CAGR of 24.9%.
Its core principles are:
- Integration: In a hyper converged appliance, the computing, storage, and networking are unified and act as a united whole. This allows each component to work together seamlessly.
- Virtualization: It employs virtualization to abstract and pool available resources. This means that all the available computing power, depositary, and network capacity are virtualized and can be allocated dynamically as needed.
- Software-Driven: It is primarily software-driven. This modifies centralized direction and allows for unparalleled automation. It replaces the need for complex, siloed hardware components — as seen in traditional storage systems.
Key Components of HCI:
- Compute:
Purpose: Provides processing power for running applications.
In HCI: Virtualized for efficient resource allocation.
- Storage:
Purpose: Stores data and eliminates traditional arrays.
In HCI: Utilizes software-defined storage for simplicity and scalability.
- Networking:
Purpose: Facilitates data communication.
In HCI: Virtualized for efficient management and assets optimization.
- Management Software:
Purpose: The Brain of HCI
In HCI: Enables automation, orchestration, and real-time monitoring of the entire infrastructure.
Integration with Software-Defined Architecture
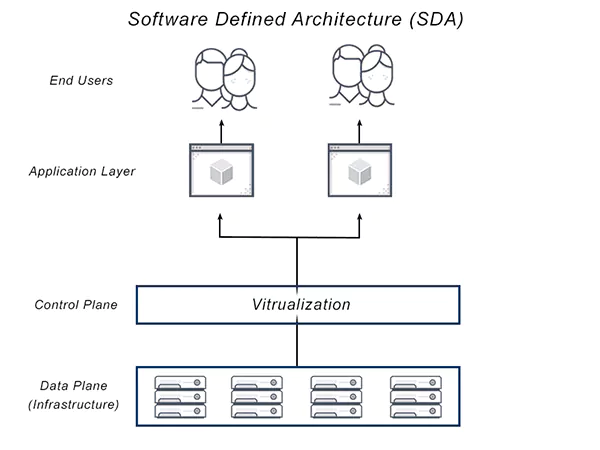
As hinted, HCI is intrinsically linked to Software-Defined Architecture (SDA). In SDA, the control plane, which decides how to handle network traffic, is separate from the data plane, the component that actually sends packets to the selected destination. This separation enhances flexibility in network management.
In that context, the software layer takes on the role of commanding the computing, storage, and networking components.
This software-centric approach enables the hyper-converged appliance to deliver greater flexibility. Resources can be allocated, de-allocated, and shifted quickly and easily.
Mixing with Software-Defined Architecture, it provides a more flexible, scalable, and manageable IT environment. This is especially beneficial for organizations aiming to modernize their data centers and make them more responsive.
Synergies between HCI and SDA: A New Paradigm
Combining both leads to a unified direction interface — this allows organizations to optimize their resources and enhance operational efficiency.
Unified Management
- In Traditional Systems: In conventional IT architectures, administration is often fragmented and requires a separate interface for computing, keeping, and networking.
- In HCI and SDA: The combination of both allows for a unified direction interface that streamlines operations and hence reduces the complexity of managing disparate systems.
Resource Optimization
Both use resource pooling technology to optimize the available computing, storage, and networking.
- Resource Pooling: Both employ resource pooling to optimize the use of computing, storage, and networking capabilities.
The Role of HCI in SDA-Enabled Data Centers
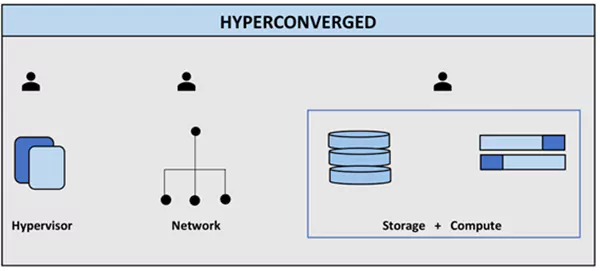
There are many features that complement the capabilities of SDA in Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC). Here is how it can complement the SDA in data centers:
Automated Orchestration
Manual processes often govern the arrangement of assets and lead to inefficiencies in traditional data centers.
However, it contributes to automated arranging by simplifying the deployment and managing the available ones. This is particularly beneficial in policy-driven automation and management.
Resource Pooling
Resources are often kept in organizations. This leads to the underapplication of the assets. When the Software-Defined Data Centers are complemented by HCI — the virtualization features complement the SDA and allow organizations to pool their assets.
Do You Know?
There are over 7,500 data centers worldwide. Amongst them, over 2,600 are in the top 20 global cities alone.
According to a study by 451 Research, 41% of respondents said they are leveraging HCI for database and data warehousing — allowing for greater flexibility and ease of management. So, organizations can operate within or alongside the hypervisor layer between the operating system and the physical storage layer.
Implications for Business
- Business Agility: Group action in SDDCs allows businesses to be more agile and adapt quickly to market changes and customer needs.
- Governance and Compliance: The automated arrangement and assets pooling features make it easier to comply with regulatory standards.
SDA’s Influence on HCI Scalability and Flexibility
Dynamic Allocation
Resource allocation is often static and requires manual intervention in traditional systems. However, HCI with SDA — organizations can enable dynamic resource allocation in HCI and allow for real-time adjustments based on workload requirements.
Network Virtualization
In traditional systems, Network pluses are rigid and hard to modify. However, by combining both — organizations can utilize the virtualization capabilities and make their network more efficient and adaptable.
Future Trends in HCI and SDA
When the current developments are enough to consider this technology in your organization, let’s see the future trends in the influence of HCI in SDA:
Cloud Integration
The trend in HCI is increasingly being integrated with cloud services and providing a cloud-like environment when maintaining closer control over IT.
- Impact on HCI and SDA: The cloud-like environment is more likely to enhance the capabilities of SDA and make this system more versatile and suitable for all types of industries.
Efficiency and Cost-Savings
The focus is on easy-to-implement solutions that can deliver significant savings quickly for many organizations. So, there is more likelihood that both evolve and become plug-and-play solutions that can be easily scaled up or down based on organizational needs.
Conclusion
Given the emerging trends like cloud integration and focus on efficiency — the future of HCI and SDA looks promising and is expected to modernize the existing IT infrastructure altogether.