- Rise of Ransomware Attacks
- Emphasis on Zero Trust Architecture
- Expansion of Cloud Security Measures
- Focus on Endpoint Security
- Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on Cybersecurity
- Evolution of Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Addressing the Challenges of Quantum Computing
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
- Conclusion

In 2024, cybersecurity encompasses an era where practices and technologies are aimed at guarding computer systems, networks, and data from cyber criminals from unauthorized entry, breaches, and attacks.
Be it a small startup or a multinational corporation, every organization is susceptible to cyber threats, making proactive security measures imperative.
Working with advanced AI tools and intricate social engineering tactics are new means to protect data from many online dangers.
Today, businesses of all sizes, corporate entities, organizations, and even governments are making the most of this advancement. How? For example, businesses rely on digital platforms to conduct their operations and store vital information.
Preventative measures open up a multitude of possibilities beyond merely protecting against potential threats.
Carry on reading to learn about the top trends that businesses need to be vigilant about in 2024, as they navigate the landscape and strive to fortify their digital defenses.
Rise of Ransomware Attacks
High-profile ransomware incidents, such as the Colonial Pipeline attack and the Kaseya supply chain attack, have underscored the devastating consequences of such cyber threats. Beyond the immediate financial losses resulting from ransom payments, organizations may also incur reputational damage, operational disruptions, and legal liabilities in the aftermath of a ransomware attack.
To lower the probability of ransomware attacks, businesses must link up with certified individuals. Enrolling in cyber security degree programs online teaches professionals to adopt a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity.
Fast Fact:
As per the reports from 2023, the average total cost of ransomware attacks is $4.5M.
It encompasses proactive measures such as regular data backups, employee training on phishing awareness, and the implementation of robust endpoint protection solutions.
Also, organizations should have incident response plans in place to facilitate timely detection, containment, and recovery in the event of a ransomware attack.
Emphasis on Zero Trust Architecture
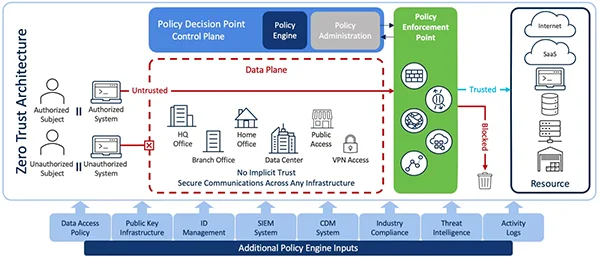
Unlike traditional perimeter-based authentication models, which rely on the assumption of trust within the network, Zero Trust architecture advocates for a “never trust, always verify” principle. This means that all users, devices, and applications, both inside and outside the corporate network, are treated as potential security risks until proven otherwise.
The growing adoption of remote work and cloud-based services has further underscored the need for Zero Trust models, as traditional network boundaries become increasingly porous.
By implementing granular login controls, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring, organizations can mitigate the risk of unauthorized entry and lateral movement by cyber attackers.
Expansion of Cloud Security Measures
The shift to remote work and the proliferation of cloud-based applications and services have expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals, necessitating enhanced safety measures.
Cloud protection encompasses a range of practices and technologies aimed at protecting data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in cloud environments.
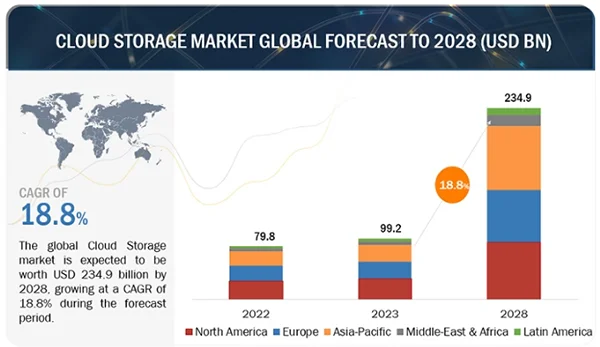
Statistics:
Back then in 2023, the Cloud Storage Market size was USD 99.2 billion. Shortly by 2028, it is expected to grow to USD 234.9 billion at a CAGR of 18.8%.
This includes encryption, identity and access management (IAM), data loss prevention (DLP), and protection incident and event management (SIEM) solutions.
By implementing comprehensive cloud protection measures, associations can safeguard sensitive information, maintain compliance with regulatory requirements, and mitigate the risk of cloud-related threats such as breaches and account hijacking.
Focus on Endpoint Security
With the rise of remote work and the proliferation of mobile devices, endpoints have become prime targets for Internet-based attacks. Endpoint protection refers to the strategies and technologies employed to protect devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets from malware, phishing attacks, and other web-based attacks.
Endpoint defense solutions encompass a range of capabilities, including antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR), application whitelisting, and device encryption.
By deploying advanced endpoint safety solutions and implementing robust policies, organizations can detect and thwart digital threats at the device level, thereby strengthening their overall cybersecurity posture.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies are increasingly being leveraged to enhance defensive capabilities, both by defenders and attackers. AI-powered cybersecurity tools can analyze vast amounts of data, detect anomalies, and identify potential protection threats with greater speed and accuracy than traditional methods.
However, the same AI technologies can also be exploited by cybercriminals to automate and amplify their attacks, making it imperative for organizations to stay ahead of emerging hazards.
By harnessing the power of AI for threat detection, incident response, and predictive analytics, organizations can bolster their defenses against evolving digital dangers and minimize the risk of data breaches and other incidents.
Evolution of Identity and Access Management (IAM)
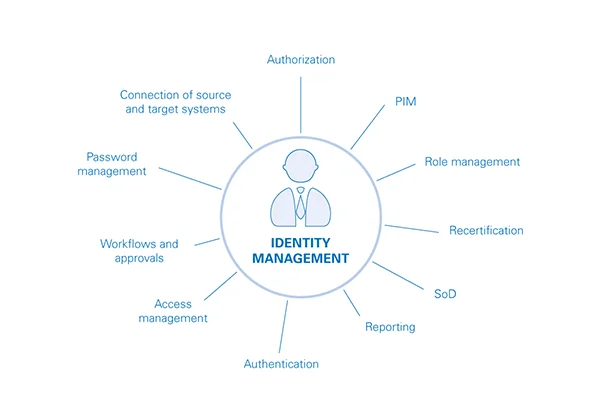
Identity and Access Management (IAM) plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and integrity of digital identities and user privileges within a company. Traditional IAM solutions focused primarily on managing user identities and controlling entry to corporate networks and applications.
However, with the proliferation of cloud-based services, mobile devices, and remote work, IAM solutions have evolved to encompass broader identity-centric approaches.
Modern IAM solutions leverage technologies such as single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and privileged access management (PAM) to enforce granular login controls and authentication policies across diverse IT environments.
By centralizing identity management and enforcing least privilege principles, institutions can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and streamline operations.
Addressing the Challenges of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing indeed holds the promise of revolutionizing various industries with its unparalleled processing power, it also poses significant challenges to traditional cryptographic algorithms used to secure sensitive data.
Quantum computers have the potential to break widely used encryption schemes, such as RSA and ECC, rendering current encryption methods obsolete.
Do You Know?:
The Quantum Computing market is expected to reach an estimated value of $1,765 million by 2025.
To address the implications of quantum computing, researchers and industry experts are actively developing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms that are resistant to quantum attacks.
These new cryptographic techniques, such as lattice-based cryptography and hash-based signatures, aim to provide quantum-safe encryption solutions capable of withstanding attacks from quantum computers.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
In an era of increasing personal information privacy regulations and cybersecurity mandates, compliance with regulatory requirements has become a top priority for a variety of businesses across industries.
Regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS impose strict requirements on the use of information protection, privacy, and safety practices, with severe penalties for non-compliance.
To ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, institutions must implement robust detailed protection policies and practices tailored to their specific industry and regulatory environment.
This includes conducting regular risk assessments, implementing sensitive information encryption and access controls, and maintaining comprehensive audit trails.
By prioritizing regulatory compliance, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to protecting customer records and mitigating legal and reputational risks.
Conclusion
By embracing cybersecurity trends such as Zero Trust architecture, cloud safety measures, and AI-powered threat detection, management can bolster their defenses against a wide range of internet-based threats.
Further, addressing insider threats, evolving IAM solutions, and leveraging automation can enhance resilience and readiness to respond to cyber-attacks effectively.
Ultimately, by prioritizing information safety investments and compliance with regulatory requirements, organizations can mitigate risks, protect sensitive information, and uphold trust and confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders.