- Understanding the Basics: What is a VPN?
- Diving Deeper: Defining VPN as a Service (VPNaaS)
- A Look at Traditional VPN Configurations
- Scalability and Deployment: VPNaaS vs. Traditional VPN
- Integration and Maintenance: Which Option is More User-Friendly?
- Security Protocols and Data Protection
- How to Determine the Right VPN Solution for Your Needs

Virtual Private Networks have been around for a very long time, trying to ensure network security and create a local network where everyone can communicate privately.
Nowadays, most people use them individually to get online privacy as when they surf the Internet through a VPN connection, they can be sure no one follows their online activities.
As you can see, VPN technology has evolved drastically in recent years, and now we have what is called a VPN as a Service (VPNaaS).
But why do we even need this transformation, especially in businesses?
Well, there are a lot of reasons why an organization would benefit more from a VPN as a Service instead of deploying their own VPN servers.
In this article, we will explain the differences between traditional VPN solutions and VPN as a Service so we can answer that question effectively.
By the end, you’ll know why you need the modern version to protect your network resources.
Understanding the Basics: What is a VPN?
Let’s first explain what a Virtual Private Network is before going to the specifics. You need to understand the concept of IP addresses first.
All online entities have a specific Internet Protocol address that defines them. It is a unique series of numbers that is used to locate a device and track its activities.
When organizations or individuals communicate on the Internet with their original IP addresses, they become vulnerable to eavesdropping and interceptions.
A Virtual Private Network simply assigns a virtual IP address that is different from the original one, so it hides network activity and lets people securely access the resources they need.
Organizations, however, need further protection than merely hiding an IP address. That’s why an organization-level VPN gateway creates a private tunnel between corporate networks and multiple devices.
They can use this VPN tunnel to ensure secure access to business resources.
VPN encrypts all the communication between two parties, further increasing the security level to ensure that even when cybercriminals access a piece of data, they are unable to read it as plain text.
It becomes nothing more than a confusing puzzle for them.
The core benefits of a VPN are privacy, security, and anonymity.
If you’re a business looking to secure sensitive data, a traveler needing to access geo-restricted content or an individual concerned about online privacy, a VPN is a versatile tool that can fulfill various needs.
DID YOU KNOW?
The global VPN market is predicted to exceed $107.6 billion by 2027
Diving Deeper: Defining VPN as a Service (VPNaaS)
An inventive method of deploying virtual private networks that has acquired a lot of attention recently is VPN as a Service or VPNaaS.
It differs from the traditional VPNs that businesses and people have become accustomed to.
VPNaaS makes VPN deployment, maintenance, and scaling easier by utilizing managed services and the cloud.
One of the defining abilities of VPN as a Service is its cloud-native nature.
Instead of having to implement a costly VPN infrastructure including hardware and dedicated IT teams, VPNaaS providers offer a ready-to-use service.
This eliminates the need for continuous maintenance since everything is handled by your VPN provider.
It also means that you can effectively secure a company’s cloud architecture as it is compatible with cloud environments.
There are also additional security features built into a VPN as a Service including built-in DDoS protection, advanced encryption protocols, two-factor authentication, and seamless updates to address emerging threats.
These additional features provide additional help to the private internet access efforts of an organization and offer protection to a company’s applications.
A Look at Traditional VPN Configurations
Before the emergence of VPNaaS, there were only traditional VPNs which were the primary method for establishing secure network traffic and communications.
These tools necessitate the deployment of a dedicated VPN infrastructure with a dedicated proxy server and a VPN client for end users.
An organization using a traditional virtual private network needs to have an IT team maintaining both the physical appliances and the software of the tool.
One of the most common types of traditional virtual private networks is the site-to-site VPN.
This configuration is used to connect two or more geographically distant locations, such as branch offices, to form a secure network.
It is a go-to solution for organizations that require constant communication and data sharing between various locations.
Another traditional setup is the remote access VPN, which allows individual users or devices to securely connect to a corporate network from remote locations.
This is especially beneficial for remote workers or employees who need secure access to company resources while on the go.
Traditional Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide total control over the network infrastructure, allowing for customization to satisfy unique security and connectivity needs.
Moreover, they are frequently the go-to option for businesses with strict compliance and data protection requirements.
With that being said, traditional VPNs are resource-intensive and require expertise in proxy configurations and hardware maintenance.
They are also both costly and complex to scale as you grow your business.
Scalability and Deployment: VPNaaS vs. Traditional VPN
One of the differentiating factors between traditional VPNs and VPNaaS is scalability and ease of deployment. Let’s see how these two solutions compare, and understand which one is better.
VPNaaS offers great scalability advantages as a cloud-based solution. Businesses can easily adjust their Virtual Private Networks through their providers to accommodate changing needs.
In case you need to onboard new users for remote access or expand network traffic, VPNaaS providers usually offer different subscription plans.
However, in terms of scalability, conventional VPN systems may be less adaptable.
Purchasing and configuring extra hardware is frequently necessary to expand a typical virtual private network infrastructure, which may be expensive and time-consuming.
VPNaaS also excels in the area of deployment speed.
A wider spectrum of customers, even those with no technical expertise, can set up a VPN with only a few clicks thanks to VPNaaS providers’ pre-configured cloud-based solutions.
On the other hand, traditional proxies usually have a more complicated setup procedure that calls for manual installs and customized configurations.
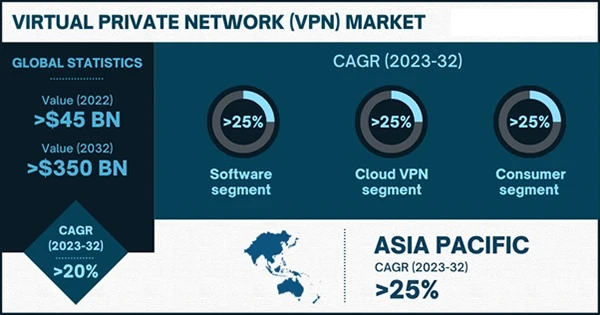
Subtitle: Virtual Private Network Market Size Forecast 2023-2032
Integration and Maintenance: Which Option is More User-Friendly?
VPNaaS solutions are highly capable of integrating with existing security infrastructure.
They can work together with multi-factor authentication and other popular technologies as a cloud-based system.
Also, they have pre-configured settings to integrate with security services with minimal expertise.
Besides integration, VPNaaS also requires almost no maintenance from the organization as a virtual private network provider sources it. They usually have 24/7 customer support for any issues and provide automatic updates.
On the other hand, maintaining and integrating older proxy settings might be more difficult. They call for constant observation, hardware control, and in-depth network expertise.
This challenge might be a headache for businesses with non-technical users or minimal IT resources. Due to the need for manual upgrades, troubleshooting, and security patch management, maintenance might potentially take a long time.
Security Protocols and Data Protection
Generally, VPNaaS provides strong security mechanisms. Modern encryption techniques, including AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), are used by VPN providers to safeguard data while it is in transit.
Many of these services provide automated updates, which guarantees that the most recent security fixes are installed as soon as possible.
Providers of VPNaaS are committed to upholding strict security guidelines as part of their offering, which makes it a dependable choice for consumers who value data security.
In traditional systems, security largely depends on the configuration and maintenance efforts of the organization.
While it provides more control over security settings, it also means that the responsibility for ensuring proper encryption, firewall rules, and security updates falls on the organization’s IT team.
This level of control can be advantageous for businesses with specific security requirements but can be challenging for those lacking in-house security expertise.
How to Determine the Right VPN Solution for Your Needs
If you’re looking for a new firewall solution and thinking of VPNaaS, you can think of the resources and expertise you have.
If you are confident that your in-house IT team is capable of configuring and deploying a dedicated virtual private network on its own, you can go for a traditional solution.
However, if you want to stay cost-effective without compromising security, and don’t want to deal with the hurdles of a traditional VPN, VPNaaS is by far the better choice right now.






