
While several specialists work on product development, the role of a UX/UI designer is considered imperative for success. A UX designer is the one responsible for designing the user experience. On the other hand, UI designers, are the ones who focus on the visual appearance of the interface.
Their team includes motion and animators, user researchers, product analysts, and UX writers. Which specialists will be included in the UX/UI Design Agency development team depends on the specifics of the project, the scale of the business, and the requirements for the finished output.
In this article, we’ll discuss the principles in the work of UX/UI designers. So, continue reading to know more.
Principles in the Work of a UX/UI Designer
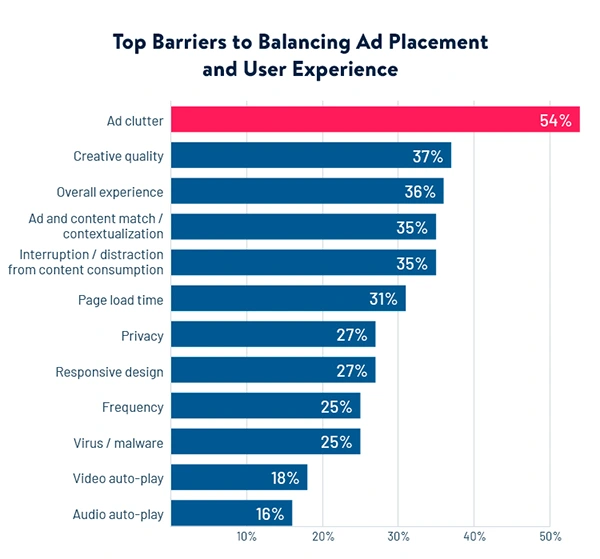
(This graph shows the top barriers to balancing ad placement and user experience, in %).
The UX/UI designer is entrusted with a significant amount of responsibilities. Their responsibilities include researching behavioral patterns, designing different variants of user experience, working out hypotheses in collaboration with other team members, and organizing interviews with potential consumers of the future brand. The result of all these activities should be the creation of a user-friendly, intuitive interface, thanks to which the people will easily solve their tasks.
The creator has a simple in essence, but rather difficult in terms of achieving the goal. To ensure that the finished product is perceived by the individual as a clear, user-friendly, and beautiful-looking tool that fully satisfies their expectations. Consumers will appreciate the finished output and will be happy to use it if the creators have followed a general rule to offer people an interface that meets several requirements.
Useful
A product will be loved if it helps a person make his/her life easier and better. For example, ordering and paying for necessary goods in a few clicks, watching a movie, looking for a repairman for household appliances, or more. This largely depends on how well a UX/UI engineer creates it.
Usable
Imagine having two similar applications on the market, for example, a budgeting app. One of them has a huge number of functions, most of which are not required by the average user, and the interface is overloaded and it takes a lot of time to find the right buttons. The other application is designed with attention to usability, it is easy to navigate and there are no unnecessary options. It makes sense that it would be more popular than the first one.
Findable
Though minor flaws are inevitable, few designers manage to create a precise product. The user should be able to quickly find a solution to a problem such as reading the manual section, referring to the FAQ section, writing in messenger, or ordering a support call. The presence of tooltips helps prevent problems caused by misunderstandings on the part of the consumer.
Credible
Many of us decide if a particular resource is worthy of attention already at the stage of our first acquaintance with it. Openly outdated design, careless execution of buttons, and ignorant combinations of colors are the reasons that can repel the modern user. The level of trust in the output, of the design of which the developers decided to save money, will be extremely low.
Desirable
Appearance is the first reason to buy many products, including digital ones. It is the UX/UI designer who determines the visual appearance of the interface. Conformity to trends, pleasant combinations of colors, and easy-to-read fonts will help the product to become popular.
Accessible
Keeping every group of users in mind, including those with physical disabilities, is another principle that guides the UX/UI engineer. If the needs of visually impaired people are taken into account, it has a positive impact on the developer’s reputation and widens the circle of loyal customers.
Valuable
The most stylish design and well-thought-out usability will not save a good that cannot satisfy the individual’s needs. An application must first and foremost solve the tasks for which it was created. Suppose, you’re developing a product for air ticket booking. Now, the primary responsibilities of the service are to provide up-to-date data on prices and current promotions, and a food ordering application.
Other Elements Affecting the Work of UX/UI Designers
With the 7 most important principles discussed in the above section, here are some other aspects worth considering while designing user experience and user interface.
- Hierarchy: Not only a good-looking or useful but a product maintained in order also matters. There are a few aspects to consider like what element or information is highly significant, what screen comes before others, etc. A design with a clear hierarchy helps consumers run tasks seamlessly.
- Flexible: The design should be flexible enough to make every user grasp easily. No matter if consumed by a newbie or an expert, the interface should be simple, so that anyone can easily navigate through the product.
- Consistency: The creator must follow a consistent approach throughout the output. This allows individuals to learn and navigate faster and more easily. Besides, it gives a sense of a minimalistic look, which is soothing to the eyes.
Conclusion
UX/UI designer is an interesting and market-demanded profession that suits people who are inclined to analytics, have a mathematical mind, but at the same time can be creative and have good taste. Thanks to the quality work of these specialists, millions of users every day with pleasure open their favorite mobile applications and solve current tasks, making their lives easier and more comfortable.
While aesthetics matters equally today, an engineer should put more focus on the product’s usability to retain loyal consumers.

