Many people use the internet every day without understanding the terms used to describe related things.
No matter if you are a tech-savvy or a common individual, you should know a few internet terms if browsing terms.
Since networks and computers are all interconnected with each other and share a vast amount of information through a protocol called TCP / IP.
These elements allow computers to communicate with each other speedily and efficiently.
In this article, we will be looking at some terms related to the internet that you should know. Be it router, modem, and switch, speed and bandwidth, latency, IP address, or URL.
Router, Modem, and Switch
You likely have heard these terms used as a handyman was installing the internet in your home or office.
The modem is a device that connects to the internet. The router creates a network inside the home while also acting as a gateway to the network.
A switch helps distribute this network connection to different devices in the home.
You can have multiple switches connected to a single router and many modern routers also come with multiple Ethernet ports that make them function as switches.
Do You Know?: The latest reports from 2023 reveal that the number of internet users worldwide stood at 5.18 billion.
They also have in-built modems, so they can function as a single unit, especially for those with few devices requiring an Ethernet connection.
Speed and Bandwidth
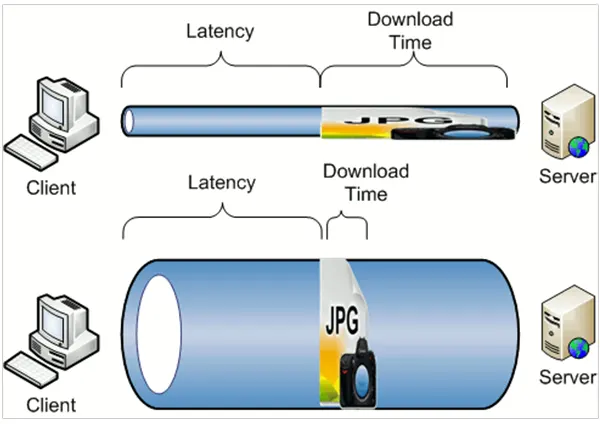
Both of these terms are often used interchangeably, but they are different.
Bandwidth refers to the total capacity available for use in data transmission (total data transmitted per unit time) when speed refers to how fast data can be transferred in a network (data transfer rate).
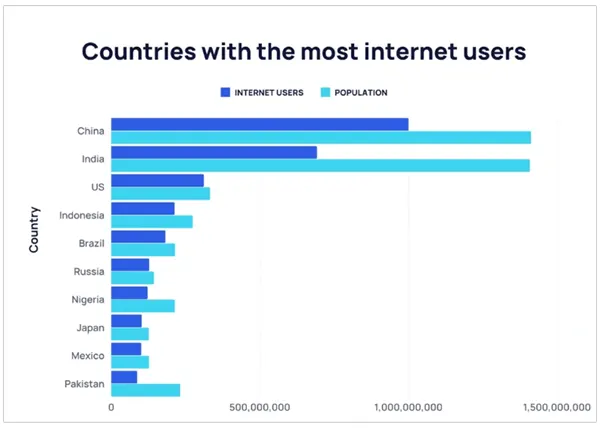
The graph above reveals China leads the way for global internet users with an estimated 1.05 billion. Moreover, nearly 74.36% of people in China use the internet.
Ideally, you want internet speeds that are as high as possible as that is the number of internet services providers use when talking about your internet connection.
Depending on the number of devices you have and how fast you want the internet to be, you can choose from a wide variety of speeds.
For example, Gateway Fiber lets you pick from speeds ranging from 250 to 1000 Mbps to satisfy all your internet needs.
Latency
From the discussion above, you would assume that networks with a higher bandwidth would have a higher data transfer rate.
That is not always the case due to latency. Latency refers to the delay data packets experience as they move through a network.
Latency is often the reason for sluggish internet performance.
There are many causes of latency, but the primary one is physics. Data packets can only move through different materials at a given speed, if passing through a copper or fiber optic cable.
For every 60 or so miles of fiber optic cabling, you get an additional 0.5 millisecond in latency. This number is higher in other mediums.
Other contributing factors include the number of hops in the connection, the delay between packet transmission (jitter), packet size, and congestion.
IP Address
Every device that can connect to the internet is assigned an address for easy identification.
This is known as an IP or Internet Protocol address. The IP address is always unique to the device, but it can change if it is dynamic or assigned permanently.
Interesting Fact: The internet is 9110 days old.
It is a unique identifier for every device or network that connects to the internet. IP addresses are assigned by an internet service provider.
Despite this, it is an online device address that can be used to communicate across the internet.
Are you aware of the fact that there are two versions of IP addresses i.e. IPv4 and IPv6?
On one hand, IPv4 is a set of four dotted decimal numbers. On the other hand, An IPv6 address represents eight groups of four hexadecimal digits. These are separated by colons.
Instances:
- IPv4 – 192.168.35.4.
- IPv6 – 2620:cc:8000:1c82:544c:cc2e:f2fa:5a9b.
URL
The Uniform Resource Locator is the web address of an internet page and file. You can use it to locate web pages or files on your computer from your browser.
URL is composed of different parts. Amongst them some are mandatory and others are optional.

It typically looks like this: https://www.example.com or file://some-file-location.
The first part of the URL is a scheme. The scheme can be both the domain and the port.
The next is “Authority”. It is separated by the scheme followed by a character pattern of:// and also includes both the domain and the port.
Path to resource comes next which represents a physical file location on the Web server. It looks like /path/to/myfile.html.
Next is “Parameters”. These are the list of key/value pairs separated with the & symbol.
The last part of the URL is “Anchor”. It is a sort of “bookmark” inside the resource. It navigates the browser to show the content located at that “bookmarked” spot.
You should now better understand the different terms used in relation to your internet connection. You might hear them once or multiple times, like URLs, for example.